U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Alarming Trends Revealed
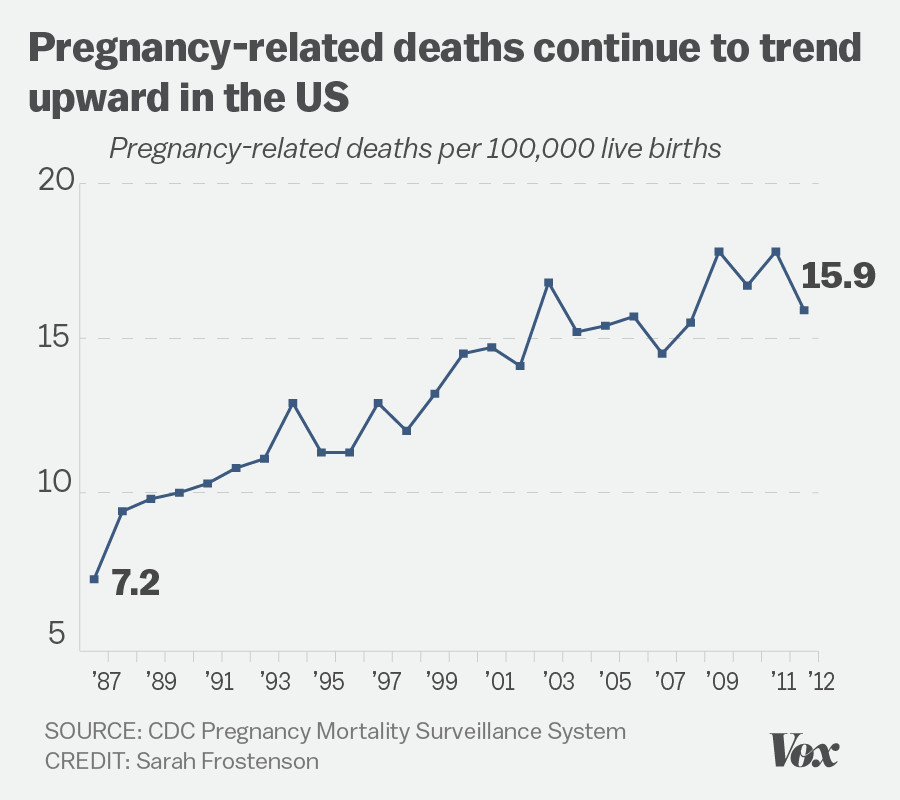
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have become a pressing concern, as the nation continues to grapple with alarmingly high maternal mortality rates compared to its high-income counterparts. Recent studies reveal that over 80 percent of these fatalities are preventable, highlighting significant failings within the healthcare system that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. From disparities in postpartum care to rising rates of cardiovascular disease in pregnant individuals, various health inequities contribute to the tragic reality that many women lose their lives due to preventable causes. The data indicates that these mortality rates have shown a disturbing upward trend, particularly during and following the COVID-19 pandemic, prompting urgent calls for comprehensive policy reform and improved healthcare access. The need for systematic changes and a focus on equitable care for all groups is essential to ensure that all mothers have the opportunity for safer pregnancies and healthier futures.
The issue of maternal health in the United States, characterized by rising rates of pregnancy-related fatalities, underscores a complex web of challenges many expectant mothers face. Alternative terms such as maternal deaths during childbirth and pregnancy-associated deaths can illuminate the serious public health crisis at hand. Despite advancements in medical technology and awareness, the stark reality is that many individuals still encounter preventable deaths in pregnancy due to inadequate healthcare access and support. Moreover, systemic issues and logistical barriers inhibit effective postpartum care and perpetuate healthcare disparities among different racial and ethnic groups. As we delve deeper into the causes and solutions concerning these maternal mortality rates, it becomes crucial to address the underlying social determinants of health to foster more equitable outcomes for all mothers.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The United States continues to grapple with an alarming rate of pregnancy-related deaths, outpacing other high-income nations. Recent statistics reveal that more than 80% of these deaths are preventable, yet systemic issues within the healthcare system persist. Factors such as inequitable access to care, varying state policies, and a lack of comprehensive postpartum support contribute to this troubling trend. As the nation struggles to address the root causes, the urgency for reform has never been more critical.
The increase in maternal mortality rates is particularly pronounced among marginalized communities, where systemic healthcare disparities have created vast inequalities in pregnancy outcomes. Data indicates that Black women and Indigenous populations face the highest risk, encountering serious health threats that could be mitigated with earlier intervention and better care access. Understanding these disparities is essential for developing targeted strategies that ensure equitable healthcare for all mothers.
The Impact of Healthcare Disparities on Maternal Mortality
Healthcare disparities in the U.S. play a significant role in the alarming rise of pregnancy-related deaths. Various factors, such as socioeconomic status, race, and geographic location, profoundly affect a woman’s access to quality care before, during, and after pregnancy. For example, maternity care deserts and insufficient healthcare infrastructure in certain states lead to inadequate prenatal and postpartum services, resulting in poorer health outcomes for mothers.
Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that includes policy reforms, community engagement, and a commitment to bias reduction within healthcare systems. By investing in comprehensive training for healthcare providers and expanding access to care in underserved areas, the nation can move closer to reducing maternal mortality rates and ensuring safer pregnancies for all women.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of such fatalities. This shift highlights the importance of recognizing chronic health conditions in expecting mothers. As rates of hypertension and other heart-related issues rise among younger women, the healthcare system must adapt to address these growing concerns effectively.
Moreover, understanding the link between cardiovascular health and pregnancy can help develop targeted prevention strategies. Implementing routine screenings, promoting healthier lifestyles, and providing education on risk factors must become standard practice in maternal care to mitigate cardiovascular risks during and after pregnancy.
Challenges in Tracking Maternal Mortality Rates
One significant challenge in addressing maternal mortality in the U.S. is the inconsistent tracking of pregnancy-related deaths. Until the full implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018, comprehensive data was lacking. This gap hindered the ability to assess trends accurately and develop informed strategies to combat rising mortality rates.
With the establishment of a more standardized tracking system, healthcare professionals can better analyze maternal mortality data and identify at-risk populations. Continued investment in research and infrastructure is essential to maintain accurate monitoring and drive policies that will ultimately improve maternal health outcomes.
The Continuing Need for Improved Postpartum Care
Postpartum care is a critical component in reducing pregnancy-related deaths, yet it often receives inadequate attention in the U.S. healthcare system. Many women face a lack of support and resources during the months following childbirth, which can lead to severe complications and even late maternal deaths. Expanding the postpartum care continuum to include mental, emotional, and physical health support is essential.
Additionally, healthcare providers need to recognize that the postpartum period extends beyond the traditional six-week check-up. By offering ongoing care and resources during the first year post-birth, healthcare systems can help identify and treat complications early, ultimately saving lives and enhancing the overall health of mothers.
Innovative Solutions to Combat Preventable Deaths in Pregnancy
As we acknowledge the staggering rates of preventable deaths in pregnancy, innovative solutions must be prioritized to address these issues effectively. Collaborations between states, healthcare professionals, and community organizations can help establish best practices that lead to improved maternal health outcomes. For instance, states like California have demonstrated that better outcomes are achievable through targeted policy changes and comprehensive healthcare reform.
Implementing telehealth services, expanding healthcare access to rural areas, and investing in community health workers can help bridge gaps in maternal care delivery. These initiatives should be funded and supported at both the state and national levels to ensure that all women receive the quality care they deserve during pregnancy and beyond.
The Importance of Community Support in Maternal Health
Community support systems play an integral role in maternal health, providing women with the resources and encouragement they need throughout their pregnancy journey. Emotional and practical support from family, friends, and local organizations can significantly impact a woman’s health and well-being. By fostering a strong community network, mothers can access vital resources that can enhance their pregnancy and postpartum experiences.
Moreover, community-based programs can focus on educating families about vital health topics, such as recognizing signs of complications or managing chronic conditions. Empowering communities with knowledge not only helps improve maternal health outcomes but also fosters a culture of support that can lead to lasting changes in perceptions surrounding pregnancy and parenthood.
Policy Changes Needed to Reduce Maternal Mortality Rates
To combat the rising rates of maternal mortality, comprehensive policy changes are necessary at both local and national levels. This includes addressing healthcare disparities and increasing funding for maternal health initiatives. Policymakers need to prioritize maternal health by investing in preventive care, expanding access to quality services, and ensuring that all women receive culturally competent care.
Furthermore, it is vital to involve mothers and advocates in policymaking discussions to address the unique challenges faced by various communities. By creating policies informed by those directly affected by maternal health disparities, the U.S. can work towards more equitable healthcare solutions that ultimately lower pregnancy-related deaths.
The Future of Maternal Health in the U.S.
The future of maternal health in the U.S. hinges on our dedication to reforming current systems and prioritizing the wellbeing of mothers. As research identifies significant factors contributing to rising maternal mortality rates, it equips leaders and practitioners with the knowledge to implement effective interventions. The growing recognition of issues surrounding racial disparities, postpartum care, and chronic health conditions are crucial for shaping ongoing strategies.
Continued advocacy and investment in maternal health education, innovative care models, and community support can lead to healthier pregnancies and improved outcomes for mothers and babies alike. As our understanding of maternal health evolves, so must our commitment to ensuring that every woman has access to safe, quality care throughout her pregnancy journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the leading causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
The leading causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths include cardiovascular disease, which has replaced hemorrhage as the main cause. Conditions such as hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and other cardiovascular disorders contribute significantly to maternal mortality rates. Addressing these chronic health issues is essential to reducing preventable deaths in pregnancy.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. maternal mortality rate is significantly higher than that of other high-income countries, with over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths being preventable. Factors contributing to this crisis include healthcare disparities, uneven access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, and systemic biases affecting minority groups.
Why are healthcare disparities a significant issue in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Healthcare disparities in the U.S. result in significant variations in pregnancy-related deaths across different racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience drastically higher maternal mortality rates compared to white women. Tackling these disparities is crucial to reducing overall maternal mortality rates and ensuring equitable healthcare access for all.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is critical for preventing pregnancy-related deaths, particularly late maternal deaths that occur between 42 days and a year after delivery. Improvements in postpartum healthcare systems can help address ongoing health issues and reduce mortality rates during this extended recovery phase.
How are chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease linked to U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Chronic diseases, particularly cardiovascular conditions, play a significant role in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths. There has been a concerning trend of younger individuals, particularly those between 25 and 39 years old, exhibiting chronic hypertension and other heart-related issues, increasing their risk during pregnancy.
What policy changes are suggested to reduce U.S. maternal mortality rates?
To reduce U.S. maternal mortality rates, policymakers need to invest in healthcare infrastructure, prioritize maternal health research funding, and develop innovative solutions to improve the quality of care during both pregnancy and the postpartum period. Addressing state-level policy discrepancies can also enhance maternal health outcomes across diverse populations.
Why is it important to include late maternal deaths in the study of pregnancy-related deaths?
Including late maternal deaths—those occurring from 42 days up to a year postpartum—in the discussion of pregnancy-related mortality provides a fuller picture of maternal health challenges. It emphasizes the need for ongoing care and support beyond the traditional postpartum period, advocating for comprehensive healthcare services for new mothers.
What changes have occurred in the data tracking of maternal deaths in the U.S.?
Since the implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018, tracking maternal deaths in the U.S. has improved significantly. This national system allows for better data collection and analysis, revealing the true scope of pregnancy-related deaths and facilitating targeted health interventions.
How does the COVID-19 pandemic relate to rising pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic has contributed to rising pregnancy-related death rates, particularly noting a sharp increase in 2021. The pandemic exacerbated existing healthcare disparities and highlighted vulnerabilities in maternal healthcare systems, necessitating urgent attention to improve overall outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. |
| Preventability | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Rising Mortality Rates | Maternal mortality rates have continued to rise from 2018 to 2022, particularly spiking in 2021. |
| Disparities in Rates | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, nearly four times higher than white women. |
| Leading Causes | Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, overtaking hemorrhage. |
| Geographical Variations | State rates vary significantly, from 18.5 to 59.7 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths are becoming more recognized, accounting for nearly a third of total deaths. |
| Need for System Reform | There is an urgent need for better healthcare systems to address pregnancy care and postpartum health. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths remain a pressing public health crisis, with alarming statistics revealing rising rates and significant disparities across racial and geographical lines. To tackle this issue effectively, it is crucial to enhance the healthcare infrastructure, focus on preventative measures, and ensure equitable access to maternal care across all demographics. Without concerted efforts and policy changes to address these disparities, the troubling trend of increasing pregnancy-related mortality in the U.S. is likely to continue.